Enterprise Resource Planning systems have become a foundational component for businesses striving to streamline operations, manage resources efficiently, and integrate various business functions. ERP systems serve as a centralized platform that unifies processes across departments, including finance, HR, supply chain, sales, and inventory management. In today’s competitive business landscape, adopting a well-suited ERP system is no longer just an option but a strategic necessity.
An effective ERP system represents more than just a collection of software tools; it embodies a holistic approach to business management. With the right ERP solution, companies gain real-time insights into their operations, optimize resource allocation, and enhance productivity across the board. As industries grow increasingly complex, ERP systems provide the agility and scalability businesses need to adapt and thrive.
For many organizations, ERP serves as the backbone of digital transformation initiatives. As businesses embrace new technologies to stay competitive, ERP systems support these efforts by providing a robust platform for innovation. From automating routine tasks to improving data accuracy and reducing operational costs, ERP systems empower companies to focus on strategic objectives and enhance their bottom line.
In this guide, we’ll explore ERP systems from various angles, covering the essential components, key benefits, implementation strategies, and emerging trends in the ERP industry. Whether you’re a small business evaluating your first ERP system or an established corporation looking to upgrade, understanding the core functions and potential of ERP can transform your approach to business management.
Understanding Enterprise Resource Planning Systems
1. What is ERP and Why Do Businesses Need It?
Enterprise Resource Planning Systems refers to a suite of integrated applications that manage and streamline core business functions. ERP systems consolidate data from various departments into a centralized database, allowing seamless information flow across the organization. This centralization minimizes data silos, reduces duplication of efforts, and improves decision-making by providing leaders with accurate, real-time data.
ERP systems enable companies to improve efficiency by automating routine tasks, such as order processing, payroll management, and inventory tracking. This automation reduces human error and frees up resources for value-added tasks. Additionally, ERP systems can be customized to suit specific business needs, offering flexibility that supports both day-to-day operations and long-term strategic goals.
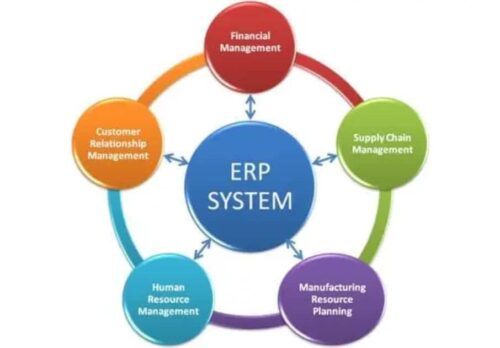
2. Core Components of an ERP System
An Enterprise Resource Planning Systems comprises several core modules, each designed to handle a specific aspect of business operations. Typical components include finance, HR, supply chain management, sales, and customer relationship management (CRM). Each module works independently yet shares data with other modules, providing a comprehensive view of the entire organization.
For example, the finance module handles accounting, budgeting, and financial reporting, while the HR module manages employee records, payroll, and benefits. The supply chain management module oversees inventory, procurement, and logistics. Together, these modules create a cohesive system that supports efficient operation and effective decision-making, enabling businesses to adapt to changing market demands.
3. Benefits of a Centralized ERP Database
One of the defining features of ERP systems is their centralized database, which houses all critical business data in one place. This centralization promotes data accuracy, as each department accesses and updates information within the same system. A unified database also enhances reporting capabilities, allowing businesses to generate comprehensive, real-time reports that inform strategic planning and performance measurement.
Centralized data storage not only improves accuracy but also strengthens security. With sensitive information stored in a single, protected location, businesses can enforce security protocols and access controls to protect against unauthorized access. This structure streamlines data management, reduces redundancy, and ensures consistent information across the organization.
4. ERP’s Adaptability to Business Growth
Enterprise Resource Planning Systems are designed to grow alongside businesses, offering scalability that accommodates expansion and changing business needs. As companies add new products, enter new markets, or expand their workforce, ERP systems can easily adapt to these changes without requiring a complete overhaul. This scalability is especially valuable for businesses that anticipate growth, as it allows them to continue using the same system while adjusting modules and functionalities as needed.
Flexible Enterprise Resource Planning Systems are also modular, meaning businesses can implement specific modules as they grow. For instance, a small company may start with finance and HR modules and add supply chain and CRM components as their operations expand. This modular approach provides a cost-effective path to digital transformation, allowing businesses to invest incrementally.
Key Strategies and Best Practices Enterprise Resource Planning Systems
1. Planning and Preparation
The success of an ERP implementation largely depends on thorough planning and preparation. Before selecting an ERP solution, businesses should outline their objectives and identify the specific challenges they aim to address. This stage includes evaluating current processes, understanding gaps, and determining how an ERP system can enhance operational efficiency.
Once objectives are defined, it’s crucial to create a roadmap that outlines the implementation timeline, milestones, and resource allocation. This preparation phase sets a solid foundation for the ERP project, ensuring that all stakeholders are aligned and that the system is tailored to the business’s unique requirements.
2. Choosing the Right ERP Vendor for Your Business Needs
Selecting the right ERP vendor is a critical decision that can impact the system’s effectiveness and overall return on investment. Businesses should evaluate vendors based on factors such as industry expertise, customization options, support services, and scalability. Researching each vendor’s reputation, understanding their service offerings, and reviewing client testimonials can help businesses make informed decisions.
A reputable ERP vendor will offer ongoing support, training, and system upgrades, ensuring that the ERP solution remains relevant as the business evolves. Additionally, choosing a vendor with experience in your industry can streamline implementation and ensure that the system meets industry-specific requirements.
3. Data Migration and Integration: Ensuring Smooth Transition
Data migration is a crucial step in the ERP implementation process, involving the transfer of data from legacy systems to the new ERP database. This process must be carefully managed to prevent data loss, ensure data accuracy, and maintain data integrity. Businesses should also verify that their ERP system integrates smoothly with existing software, such as CRM tools, accounting systems, and e-commerce platforms.
Ensuring data compatibility and establishing clear data migration protocols minimizes the risk of disruptions. Testing the integration of each module before full implementation further guarantees that the system functions as intended and that all departments have access to the necessary data.
4. Training and Change Management for Successful ERP Adoption
A successful ERP implementation requires more than just technology; it involves a cultural shift. Employees need to understand the value of the ERP system and feel comfortable using it. Providing comprehensive training ensures that users across departments can leverage the system effectively, enhancing productivity and maximizing ROI.
Additionally, businesses should implement a change management strategy to help employees adapt to new processes and system functionalities. Regular feedback sessions and open communication channels allow for continuous improvement and help address any challenges users may encounter during the transition period.
Emerging Trends and Technologies Enterprise Resource Planning Systems
1. Cloud-Based ERP
Cloud-based ERP systems have gained popularity due to their flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and accessibility. Unlike traditional on-premises ERP systems, cloud-based solutions are hosted online, allowing businesses to access their ERP data from anywhere with an internet connection. This accessibility is particularly advantageous for businesses with remote teams or multiple locations.
Additionally, cloud-based ERP systems are typically more affordable, as they eliminate the need for expensive hardware and reduce maintenance costs. With automatic updates, businesses can also ensure that their ERP system stays current with the latest features and security protocols, providing a scalable solution for long-term growth.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning in ERP
AI and machine learning are transforming ERP systems by enhancing automation, predictive analytics, and data processing. With AI, ERP systems can automatically detect patterns in data, provide insights into customer behavior, and even predict inventory needs. These capabilities help businesses make proactive decisions, optimize processes, and improve service quality.
Machine learning also enables ERP systems to personalize user experiences, as it continuously learns from data inputs and adapts to user behaviors. This trend represents the future of ERP, where intelligent systems support decision-making and streamline complex tasks across the organization.
3. IoT Integration with ERP for Enhanced Supply Chain Management
The Internet of Things (IoT) has a growing impact on ERP systems, particularly in the realm of supply chain management. By integrating IoT sensors with ERP systems, businesses can track inventory levels, monitor equipment health, and even predict maintenance needs in real-time. This real-time monitoring reduces downtime, optimizes resource allocation, and enhances the efficiency of supply chain operations.
For businesses with extensive supply chains, IoT-enabled ERP systems provide visibility into every aspect of the process, from raw material sourcing to final delivery. This visibility allows companies to respond quickly to changes in demand, minimize stockouts, and ensure timely order fulfillment.
4. Data Security and Privacy in ERP Systems
As ERP systems handle sensitive business and customer data, data security has become a top priority. Businesses must ensure that their ERP systems comply with data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, to protect against breaches and maintain customer trust. Advanced encryption, user authentication, and regular security updates are essential features of a secure ERP system.
Implementing data security best practices also includes educating employees on data handling and access protocols. By fostering a culture of security and responsibility, businesses can safeguard their ERP data and prevent unauthorized access.
Conclusion
Adopting an ERP system can be transformative for businesses aiming to enhance efficiency, streamline operations, and drive growth. With the right ERP solution, companies gain access to powerful tools and insights that support strategic decision-making and operational resilience. As ERP technology continues to evolve, businesses that invest in ERP systems will be well-positioned to thrive in an increasingly complex and competitive marketplace.
FAQ Section
- What is ERP in simple terms?
ERP is a software solution that integrates various business processes into a single system, allowing departments to share data and collaborate efficiently. - How does ERP benefit small businesses?
ERP helps small businesses improve efficiency, reduce errors, and manage resources effectively by centralizing data and automating processes. - Can ERP systems be customized?
Yes, ERP systems can be tailored to meet specific business needs, ensuring that companies have the functionality they require. - What is the difference between cloud-based and on-premises ERP?
Cloud-based ERP is hosted online and offers remote access, while on-premises ERP is installed locally on a company’s servers. - How does ERP improve customer service?
By consolidating data, ERP systems provide customer service teams with a comprehensive view of customer history, enabling faster response times. - Is ERP implementation costly?
The cost depends on the system, but ERP generally requires investment in both software and implementation. However, long-term savings in efficiency often justify the expense. - What are the risks of not using ERP?
Without ERP, businesses may face data silos, reduced efficiency, increased errors, and challenges in adapting to growth.